- ligand gated channels neurotransmitters - voltage gated channels transmembrane potential electric field - second messenger gated channels nucleotides G-proteins. Either passive or active 3.

Ion Channel Learn Science At Scitable
Functionally unique Page 4.

. Voltage-gated Na channel- These channels are responsible for the generation of action potentials. An activation gate that needs stimulation in order to open and allow sodium ions to enter the cell and an inactivation gate that closes stopping the entry of sodium ions. Light blue Ca V and Na V.
Light green TRP channels. Ligand-gated ATP activated Cl- channels. Ion Channels Are Selective Ion channels are selective.
Two types of voltage-gated channels contribute to the action potential. Ion channel coupled receptors are involved in rapid signaling between. Ion channels can be classified according to which chemical or physical modulator controls their gating activity.
Sodium ion channels have two independent gates. Ion channels function as pores to permit the flux of ions down their electrochemical potential gradient. Voltage-gated potassium channels Kv Sodium channels Nav Calcium channels Cav.
Primary transporters symporters and antiporters are the three types of transporters. They move different types of molecules B. A cation is formed by the loss of one or more electrons by an atom.
Thus we have different groups of channels as summarized below. Hormone Signaling Via G ProteinCoupled. Nerve function is entirely based on this fact.
Ion channels are involved in the passive transportation of ions. In solution ions are stabilized by polarized water molecules in the surrounding environment. Light orange K V 1012 channels and cyclic nucleotidemodulated CNG and HCN channels from Yu and.
Several families of ion channels are gated by extracellular ligands Hille 2001. Voltage-gated channels respond to perturbations in cell membrane potential and are highly selective for a specific ion ie Na K Ca2 and Cl-. Narrow highly selective ion channels mimic the water environment by lining the conducting pore with polarized carbonyl oxygen atoms.
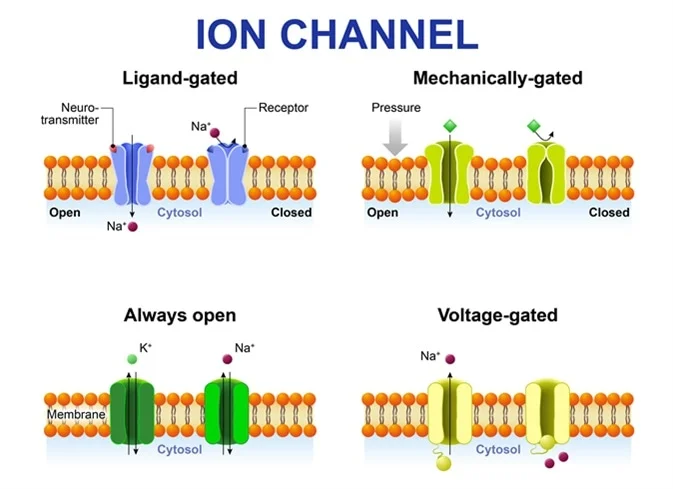
The mechanically gated channels that are ion channels whose. Distinguish between types of ion channels Ion channels can be 1 voltage-sensitive 2 ligand-gated or 3 respond to physical stimuli. A positively charged ion is known as cation.
The opening of ion channels alters the charge distribution across the plasma membrane. Other K selective channels with pore-forming P domains. 2 The permeability of voltage-gated ion channels is influenced by the membrane potential.
These ion channels have gates that open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. On the basis of localization ion channels are classified as. As the name implies the activity of voltage-gated channels is regulated by changes in the transmembrane.
The opening and closing of the channels are triggered by changing ion concentration and hence charge gradient between the sides of the cell membrane. Ligand-gated channels activated by ACh GABA or Gly. Background colors separate the ion channel proteins into related groups.
They allow some ions to pass through and prevent the passage of others. Prominent among these are the cysteine-loop channels of fast chemical synapses specialized as receptors R for the chemical neurotransmitter acetylcholine ACh glycine gly gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA or serotonin 5-HT. Naand Ca2 channel subunits cross the membrane 24 times Figure 47AB and the channel is evidently formed by just one of these Naor Ca2channel subunits.
Ion Channel Ion Channels. Less-selective channels form pores with a diameter large enough that ions and water molecules may pass through together. Voltage-gated ion channels and ligand-gated ion channels are two types of gated ion channels.
Gastrointestinal Hormones and Neurotransmitters. Ion channels transport ions through a concentration or electrochemical gradient. There are three different functions of these channels.
Light red potassium channels except K V 1012 which have a cyclic nucleotidebinding domain and are more closely related to CNG and HCN channels. The ability to gate an ion channel allows electrical energy to be built up inside the cell. Like the bacterial Kchannel the membrane-spanning domains of all ion channels appear to form a central porethrough which ions can diffuse Figure 48.
But there are at least nine genes coding for different versions of the first type of subunit and at least three coding for different versions of the second with further diversity due to alternative. Ion channels come in many different types some of which are selective for. Na K Ca2 and Cl ions mostly move through ion channels.
Ion channels can be either non-gated or gated. Voltage-gated potassium channels Kv Sodium channels Nav Calcium channels Cav and Chloride. A channel protein does not need energy C.
In fact a majority of ion channels fall into these two broad categories. The action potential arises because the plasma membranes of excitable cells have special voltage-gated channels. Ion channels control the movement of ions through the neuronal cell membrane.
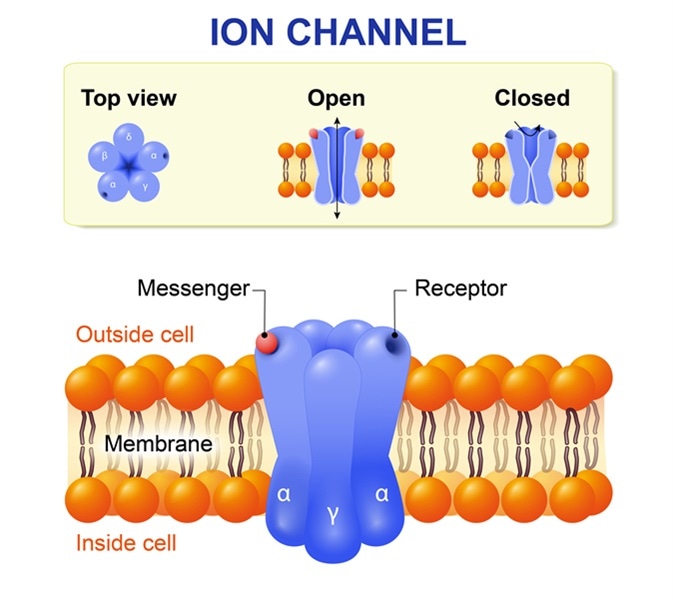
1 Ligand-gated ion channels open when a chemical ligand like a neurotransmitter binds to the trans-membrane protein. The channels are. Sodium potassium and calcium ion channels are the most important types of voltage-gated ion channels.
Recall that the ionic composition of the cytoplasm is quite. Channel proteins are. The voltage-gated channels that are gated by changes in membrane potential.
Voltage-gated ion-channels are usually ion-specific and channels specific to sodium Na potassium K calcium Ca 2 and chloride Cl ions have been identified. Depending on the factor s that produce their opening and closing gating ion channels are classified into four types. They are further subdivided into families based on the major permeant ion.
Active and passive transportation are two modes where cells transport ions across the plasma membrane. There are two types of ions. The ions of all the metal elements are cations.
Conclusion Ion channels and transporters are two types of transmembrane proteins involved in the movement of ions across the cell membrane. Plasma membrane channels Examples. Answer to Question 1.
Sodium atom loses 1 electron to form a sodium ion Na which is cation. Ions like k Na Ca and molecules such as glucose ATP proteins m-RNA continuously move in and out of the cell. The ligandgated channels that are regulated by ligands ie chemicals that bind to it.
Vertebrate neurons for example have acetylcholine-gated ion channels that differ from those of muscle cells in that they are usually formed from two subunits of one type and three of another. Potassium channels and sodium channels. A channel protein does not bind the molecules it transports.
Importance Of Ion Channels In The Body

Types Of Ion Channels Leak Channels Ppt Video Online Download
0 Comments